When it comes to the legal system, you might often hear about both state and federal courts—but what exactly sets them apart? While they work side by side to uphold the law, each plays a unique role with distinct powers, procedures, and areas of focus. Whether you’re a curious citizen, a student, or just someone intrigued by how justice is served, diving into the differences between state and federal courts reveals a fascinating world where jurisdiction, case types, and even judges’ appointments all play a part. Let’s explore what makes these two court systems tick and how they shape the legal landscape in the United States.
Table of Contents
- State and Federal Courts Explained How Jurisdiction Shapes Your Case
- Diving Into Procedures How State and Federal Courts Handle Trials Differently
- When Should You Choose State Court versus Federal Court Tips for Making the Right Decision
- Understanding Appeals Navigating the Paths in State and Federal Court Systems
- In Conclusion
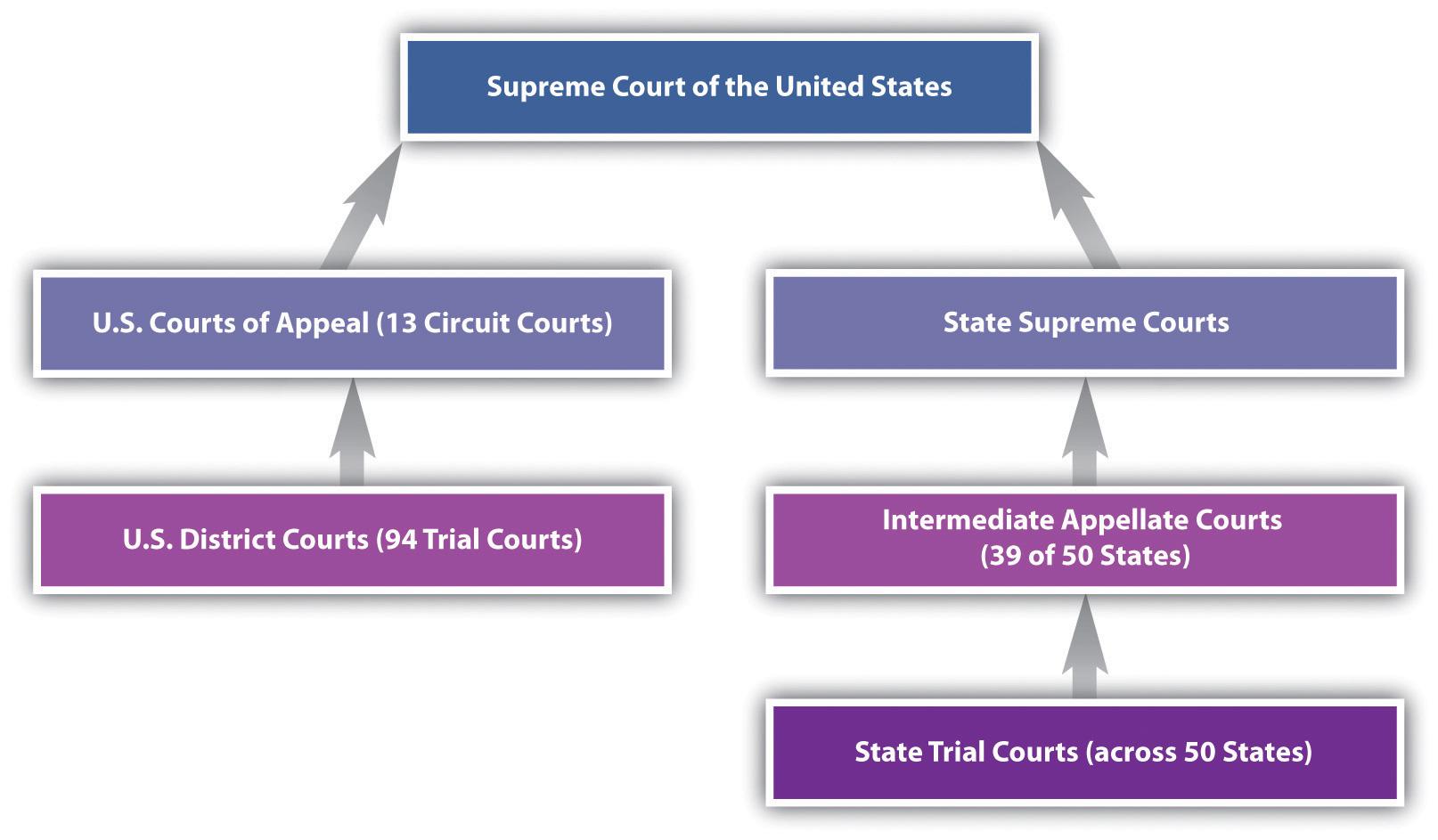
State and Federal Courts Explained How Jurisdiction Shapes Your Case
Understanding where your case will be heard is crucial because jurisdiction dictates the authority a court has to make legal decisions. State courts generally handle matters involving violations of state laws, such as family disputes, traffic violations, and most criminal cases. These courts have broad jurisdiction, meaning they can hear a wide variety of cases unless specifically reserved for federal courts. On the other hand, federal courts are created by the Constitution and are limited in scope, typically dealing with issues involving federal laws, constitutional questions, or disputes between parties from different states.
Jurisdiction not only determines the court’s authority but can also influence the legal procedures, potential outcomes, and even the timeline of your case. For example, federal courts often follow stricter procedural rules, which can affect the way evidence is introduced or how appeals are handled. Additionally, certain cases like bankruptcy, patent law, or federal crimes can only be brought in federal court, highlighting how the subject matter profoundly shapes where your case is heard.
- State Courts: Broad jurisdiction with many case types, including probate, family, and contract disputes.
- Federal Courts: Limited jurisdiction, focusing on federal statutes, constitutional rights, and cross-state controversies.
Diving Into Procedures How State and Federal Courts Handle Trials Differently
When it comes to navigating the trial process, state and federal courts diverge in fascinating ways. For starters, state courts typically preside over a broader range of cases — from minor disputes like small claims and traffic tickets to serious criminal charges. Federal courts, however, focus on cases involving federal laws, constitutional questions, or disputes between states or diverse parties. This distinction shapes the trial procedures, where state courts often have more flexible rules tailored to the community’s needs, while federal courts adhere strictly to the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure and Evidence, emphasizing uniformity and consistency across the nation.
Another interesting facet lies in the jury selection and trial timelines. In federal courts, the jury pool is drawn from a wider geographic area, commonly making for a more diverse jury and sometimes longer jury selection processes. State courts, on the other hand, tend to pull jurors from narrower, often more localized districts, potentially speeding up the process but changing the composition of the jury dramatically. Also, federal trials can be lengthier due to more detailed discovery rules and procedural safeguards. Here’s a snapshot of key procedural contrasts:
- Filing Procedures: Federal courts require strict adherence to filing deadlines and specific formats, while states may allow more lenient filing protocols.
- Pretrial Motions: Federal judges tend to be more proactive in managing pretrial motions such as summary judgment, often shortening trials.
- Appeal Routes: Federal trial court decisions generally appeal directly to a federal appellate court, whereas state court appeals may follow a more layered trajectory.
- Evidence Rules: Although both systems aim for fair evidence rules, federal courts’ guidelines can be more rigid and technical.
When Should You Choose State Court versus Federal Court Tips for Making the Right Decision
Deciding between state and federal court often hinges on the nature of the case and the legal questions involved. State courts have broad jurisdiction, handling the majority of civil and criminal cases that arise under state laws, such as family disputes, property issues, and most contract cases. If your case involves state statutes or local ordinances, or if the dispute centers on state constitutional matters, state court is usually the natural choice. Additionally, state courts tend to be more accessible for everyday legal issues, providing more options for jury selection and faster resolutions in many instances.
On the other hand, federal courts are the playground for cases involving federal laws, constitutional questions, disputes between citizens of different states (diversity jurisdiction), or cases where the United States government is a party. If your case raises complex questions of federal law, involves large sums in controversy, or needs to address nationwide issues, federal court might be the strategic arena. Consider these factors:
- Jurisdiction: Does the issue arise under federal or state law?
- Parties involved: Is there diversity of citizenship or a federal party?
- Case complexity and stakes: Would a federal judge or jury be better suited for an issue impacting broader legal principles?
Understanding these nuances can guide you to the forum that not only fits the letter of the law but also serves your case’s practical needs.
Understanding Appeals Navigating the Paths in State and Federal Court Systems
When a court decision doesn’t go your way, understanding the appeal process is key to determining your next move. Appeals in both state and federal systems serve the essential function of reviewing lower court rulings for legal errors—however, the routes they take can vary significantly. In state courts, appeals often begin in an intermediate appellate court where judges scrutinize the application of state law and procedural fairness. On the other hand, federal appeals navigate through circuit courts, focusing on interpretations of federal statutes, constitutional issues, and regulations. Recognizing which system handles your appeal helps unravel the complexity and tailor your legal strategy effectively.
Delving deeper, there are some fascinating distinctions to keep in mind:
- Scope of Jurisdiction: State courts often deal with a wide array of cases from local crimes to family law, while federal courts handle disputes involving federal laws, interstate matters, and constitutional questions.
- Procedural Nuances: Federal appeals generally follow the Federal Rules of Appellate Procedure, which can be more stringent compared to each state’s unique guidelines.
- Pathways to Higher Courts: While state appeals can ascend to a state supreme court, federal appeals might reach the U.S. Supreme Court, though only a small fraction of cases are accepted.
Navigating these paths effectively means knowing not only the legal grounds but also appreciating the procedural landscape that differentiates state from federal appeals.
In Conclusion
Whether you’re a casual observer or a budding legal enthusiast, exploring the distinctions between state and federal courts opens a fascinating window into how justice is administered across the U.S. Both court systems play vital roles, each with its own rules, scopes, and quirks that shape our everyday lives in subtle but significant ways. Next time you hear about a court case on the news, you might find yourself wondering: is this a matter for state or federal court? The answer could reveal a lot more about the story than you initially thought. Stay curious, and keep diving into the layers of our complex legal landscape!